BIM USE
BIM (Building Information Modeling) is simply the modeling of building information or data.BIM brings together a collaborative working method as well as a 3D digital model containing intelligent and structured data. It is this model that will transcribe the physical and functional characteristics of the building and the infrastructure.
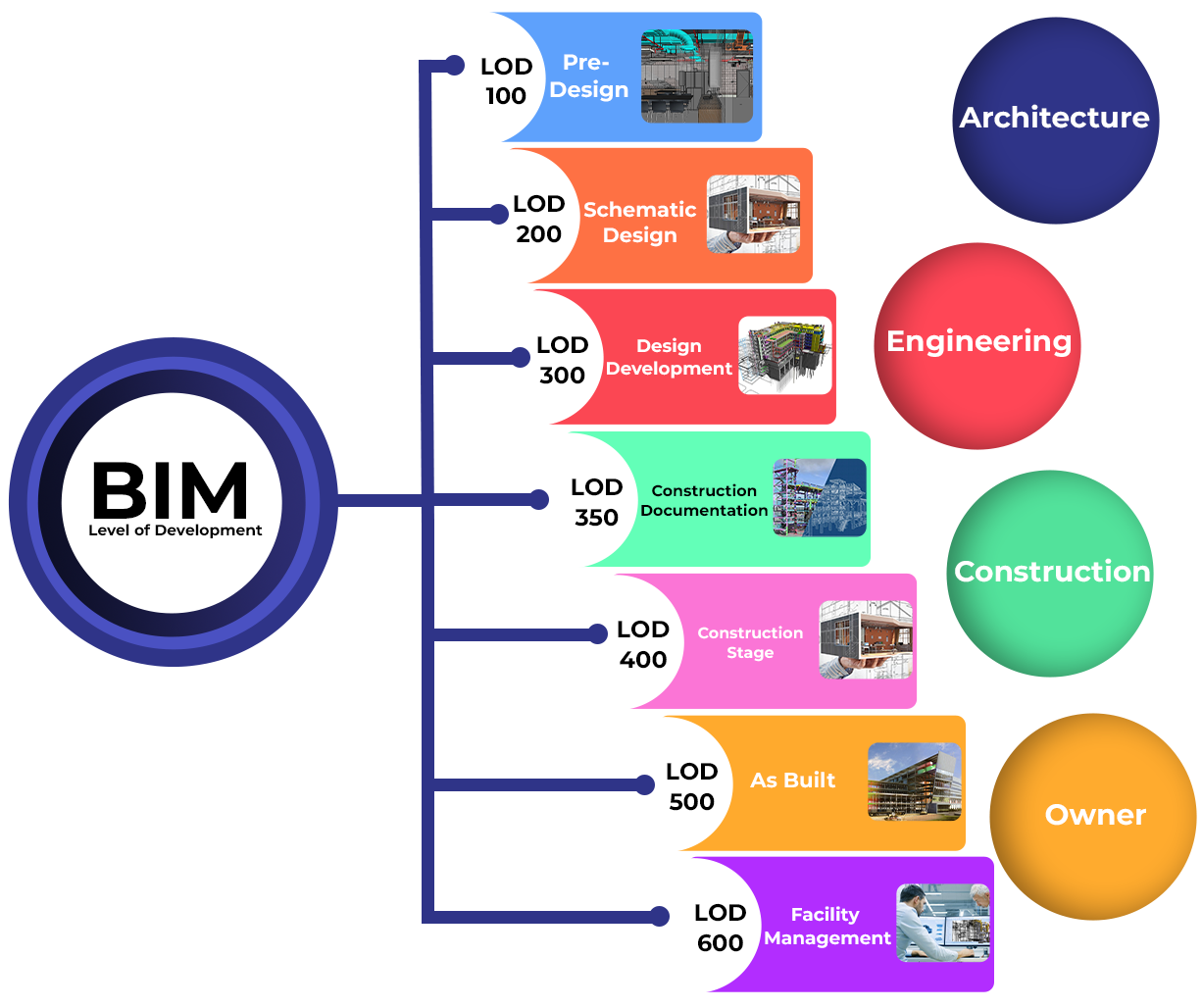
What are BIM dimensions?
The creation of BIM dimensions was prompted by the need to distinguish between modelling geometry in two and three dimensions. This development has taken place as modelling has progressed from sketchbooks to the earliest 2D CAD systems to 3D modelling software.
By integrating more elements in their modeling, project teams may find it simpler to comprehend the data they are attempting to portray. 4D is sometimes described as "modeling schedule information to model construction sequences." 5D is referred to as "adding financial cost." There isn't much worldwide consensus beyond this, and it may be argued that cost is only an additional data point and not at all a "dimension."
International standards typically contain these dimensions. Instead of using phrases like 5D, 6D, or 7D, etc., it is much preferable to be clear about the exact information that has to be simulated.
For instance, if the hiring party demands that information about sustainability, inclusive design, fire safety, and health and safety be simulated, the project team should be given specific information needs. Additionally, they must describe precisely what fields and formats of data are required.Having stated that, this article examines the "dimensions of BIM" that are more frequently employed. They might be helpful to introduce the various BIM use cases to clients, to start talks with them, and to assist build more specific requirements.
2D BIM
A 2D BIM is a digital geometric model that includes an information-related X and Y axis. Early CAD systems were 2D models, allowing for the quicker and more accurate development of plans and sections on a computer than manually on a drawing board.
Parameters, restrictions, and concepts can now be connected to the 2D model thanks to more sophisticated modelling tools. However, few professionals in the field would classify 2D geometric models as BIM.
3D BIM
A digital geometric model called a 3D BIM has an X, Y, and Z axis that is linked to other information. Tools for 3D modelling have achieved great success because:
All of these characteristics significantly increase precision and effectiveness while lowering the possibility of project faults.
Further advantages can be observed where relevant information is linked or contributed to these models.
In order to give a larger collection of coordinated information, we additionally urge specification information to be linked to the objects. if a cloud tool is used to store specification data. While still managing and reporting on a complicated information set, this offers the advantage of keeping the 3D model more straightforward.
4D BIM
Sequences of model construction now include scheduling information thanks to 4D BIM. The project team can more clearly picture how the construction will be done by including a time dimension. From the perspective of a contractor, this is crucial. When 4D BIM was first made available through the use of new modelling technologies, it represented a significant advancement for the industry since it showed collaboration between the design and construction teams through the coordination and exchange of 3D models.
5D BIM
In general, 5D BIM is seen as enhancing a model with cost data. It is advisable to clearly outline these particular criteria while talking about 5D BIM. Is the team expected to cover operating or capital costs, for instance? Are these figures supposed to be records of as-built costs or pre-tender estimates? Who is in charge of including this information? Which measurement technique is to be applied?
6D BIM
Some people believe that facility management is being added to the information provided by 6D BIM. However, there isn't much industry agreement on this, and this might not even be a "dimension" at all. It is highly recommended to spell out exactly what is needed when talking about 6D BIM so that everyone involved is on the same page.
7D BIM
Some people believe that 7D BIM expands the information set by include sustainability information. Be sure to precisely define the necessary information in terms of data types, scope, units, norms of measurement, etc., just as you would with 6D BIM.
8D BIM
Some people believe that 8D BIM is expanding the knowledge set by including health and safety information. Be sure to precisely define the necessary information in terms of data types, scope, units, norms of measurement, etc., just as you would with 6D BIM.

